Report•October 9, 2025
Monthly Attribution Overview – September 2025
An analysis of how climate change boosted United States temperatures in September 2025
Using Climate Central’s Climate Shift Index (CSI) tool to measure the impact of climate change on daily temperatures across the United States, as well as NOAA’s Applied Climate Information System (ACIS) to find daily temperature information, we have compiled a high-level overview of how climate change has affected temperature trends in September in cities across the United States. (Dataset downloadable as Excel workbook here.)
1. High-Level Findings
Long-term September warming trends show that nearly all cities analyzed have gotten warmer since 1970, consistent with findings from Climate Central’s 2025 Summer Package.
The U.S. saw elevated temperatures in September with an average anomaly of 1.5°F across 192 cities.
Eleven cities experienced one of their top five warmest August temperatures on record. On average, stations have data reaching back to 1893.
Elevated Climate Shift Index values were observed across the U.S. in the South, Ohio Valley, Upper Midwest, Northern Rockies & Plains, Northwest, Southwest, and West (regions defined by the NCEI climate regions).
Eureka, CA; Honolulu, HI; San Francisco, CA; and San Juan, PR all experienced at least two weeks' worth of CSI values of 2 or higher, indicating a strong climate change influence.

Figure 1. Threaded ACIS temperature anomalies for September 2025 relative to the 1991-2020 standard normal period. Analysis based on ACIS data.
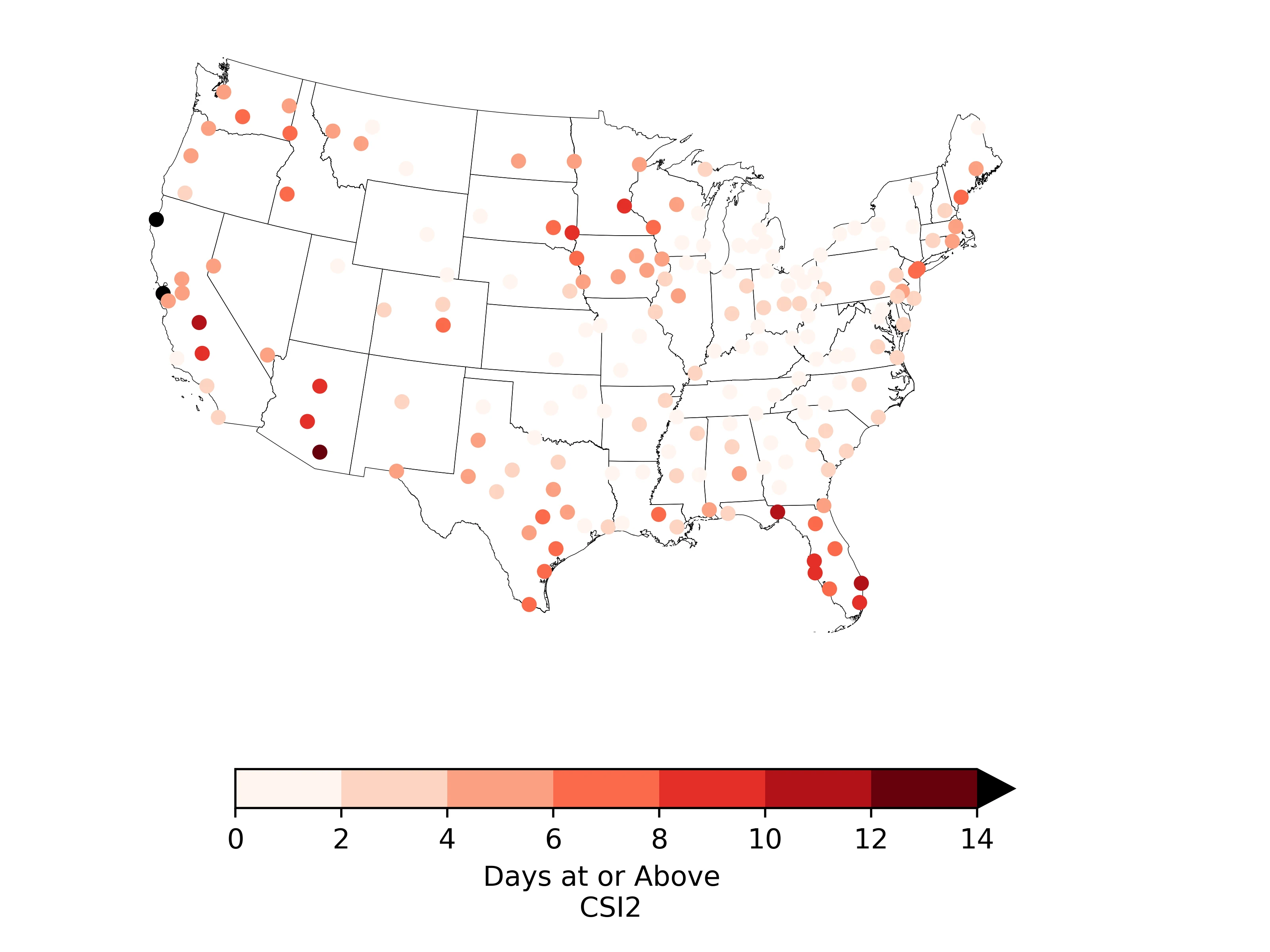
Figure 2. Days with a CSI of 2 or higher for September 2025 for ACIS threaded stations. Analysis based on ERA5 data (6/01 - 5/25) and GFS data (6/26-6/30).
2. Local Temperature Anomaly Analysis
The average temperature anomaly across the 192 cities analyzed was 1.5°F, with a large majority — 161 cities — having hotter-than-average temperatures.
Temperatures were moderately elevated across the country, with nearly every region experiencing positive temperature anomalies, or differences from normal. The region that experienced the most unusual heat was the Northwest (states in this region include Washington, Oregon, and Idaho). The average temperature anomaly was 3.42°F. The region with the smallest difference from normal was the Southeast, where temperature anomalies were 0.15°F cooler than average.
The most unusually warm city this September was Spokane, WA, which was 7.8°F warmer than usual.
Of the 191 ACIS stations analyzed, 190 showed positive temperature trends for September, indicating that these cities have been warming on average since 1970.
Reno, NV, warmed the most out of all the analyzed cities. The average September in Reno is 10.8°F warmer than it was in 1970.
Table 1. Top 10 ACIS stations with the highest September 2025 temperature anomaly.
City | State | Temperature Anomaly (°F) | Average Temperature (°F) | Warming Since 1970 (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Spokane | WA | 7.8 | 69.1 | 6.2 |
Missoula | MT | 6.7 | 64.4 | 5.8 |
Great Falls | MT | 6.2 | 63.6 | 3.5 |
Lewiston | ID | 5.6 | 71.7 | 4.8 |
Yakima | WA | 5.6 | 67.9 | 4.8 |
Rapid City | SD | 4.8 | 66.3 | 4.4 |
Boise | ID | 4.4 | 70.9 | 7.9 |
Helena | MT | 4.4 | 63.5 | 8.5 |
Bismarck | ND | 4.1 | 64.0 | 6.8 |
Billings | MT | 3.9 | 65.6 | 6.5 |
Table 2. Top 10 ACIS stations with the fastest warming September since 1970.
City | State | Warming Since 1970 (°F) | Temperature Anomaly (°F) | Average Temperature (°F) |
Reno | NV | 10.8 | 2.3 | 69.6 |
Helena | MT | 8.5 | 4.4 | 63.5 |
Boise | ID | 7.9 | 4.4 | 63.5 |
Duluth | MN | 7.6 | 1.6 | 59.1 |
Minneapolis | MN | 7.6 | 3.6 | 67.4 |
Salt Lake City | UT | 7.4 | 3.8 | 72.4 |
Wheeling | WV | 6.9 | 2.1 | 67.3 |
Bismarck | ND | 6.8 | 4.1 | 64.0 |
Las Vegas | NV | 6.8 | -0.3 | 83.6 |
Colorado Springs | CO | 6.7 | -0.6 | 62.6 |
3. Local Climate Shift Index Analysis
San Juan had 22 days at CSI 5 in September, indicating that temperatures on those days were at least five times more likely because of climate change.
Twenty-eight cities across the country experienced at least a week of days at, or above, a CSI of 2.
On average, cities in the West experienced the highest number of days — eight — with a CSI of 2 or above.
Table 3. Top 10 ACIS stations with the highest number of days at or above a CSI of 2 during September 2025.
City | State | Days at CSI = 2 or higher | Days at CSI = 5 | Average Temperature (°F) | Temperature Anomaly (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
San Juan | PR | 25 | 22 | 83.9 | 0.5 |
Honolulu | HI | 25 | 11 | 82.6 | 0.9 |
San Francisco | CA | 18 | 0 | 67.3 | 2.0 |
Eureka | CA | 15 | 0 | 60.0 | 2.8 |
Tucson | AZ | 13 | 5 | 84.3 | 1.4 |
West Palm Beach | FL | 12 | 7 | 82.7 | 0.8 |
Juneau | AK | 11 | 0 | 52.8 | 2.6 |
Tallahassee | FL | 11 | 3 | 78.7 | -0.5 |
Fresno | CA | 10 | 3 | 79.3 | 2.1 |
Orlando | FL | 10 | 7 | 81.8 | 0.8 |
Flagstaff | AZ | 9 | 2 | 59.0 | 0.7 |
METHODOLOGY
Calculating the Climate Shift Index
All Climate Shift Index (CSI) levels reported in this brief are based on daily average temperatures and ERA5 data. See the frequently asked questions for details on computing the Climate Shift Index, including a summary of the multi-model approach described in Gilford et al. (2022).
City Analysis
We analyzed 191 Applied Climate Information System (ACIS) stations associated with U.S. cities. For each city, we found the CSI time series from the nearest 0.25° grid cell. We calculated the number of days at CSI levels 2, 3, 4, and 5. We used ACIS data to find the average monthly temperatures, temperature anomalies, and precipitation information, and to derive average monthly warming trends for each city.
